Introduction
As businesses adopt AI to improve search, customer support, analytics, and automation, one question appears again and again:
Should we use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) or fine-tuning?
Both approaches help Large Language Models (LLMs) perform better on specialized tasks, but they solve very different problems. Understanding when to use each is essential for building high-performing, reliable, and cost-effective AI applications.
At a high level:
RAG = Teach the model by giving it the right documents at the right time.
Fine-tuning = Teach the model by modifying its internal parameters.
Although this difference seems simple, the decision has major implications for accuracy, maintenance, scalability, privacy, and cost. This article explains both methods in beginner-friendly language and offers a clear framework for deciding which one fits your use case.
1. What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation enhances an LLM by allowing it to look up external information before producing an answer. Instead of relying only on its own training data, the model retrieves relevant documents from a knowledge base and grounds its response in that information.
How RAG Works (Step-by-Step)
User asks a question.
The system converts the question into a vector (embedding).
It searches a vector database for the most similar documents.
Relevant text is fed into the LLM.
The model generates an answer using both retrieved context and its own reasoning abilities.
This makes RAG powerful for tasks where accuracy depends on having the latest, private, or domain-specific information.
Why RAG Matters
Because LLMs cannot store every detail of your business inside their parameters, retrieval gives them “live access” to your knowledge. This allows you to update information instantly without retraining a model.
RAG is ideal when your data changes frequently or when your responses must be grounded in real facts instead of the model’s memory.
2. What Is Fine-Tuning?
Fine-tuning changes the model itself. Instead of retrieving outside information, you modify the model’s internal weights so it learns a new style, domain, or behavior.
How Fine-Tuning Works
-
Collect labeled examples of the behavior you want.
-
Use supervised training to update the model’s parameters.
-
Deploy the new “specialized” model.
-
The model now performs tasks more consistently and with fewer prompts.
Fine-tuning is powerful when you want the AI to behave differently, not just access different information.
What Fine-Tuning Improves
-
Tone and writing style
-
Response format
-
Domain-specific phrasing
-
Classification behavior
-
Task-specific reasoning patterns
-
Ability to follow instructions with fewer tokens
Unlike RAG, fine-tuning does not give the model updated knowledge. Instead, it shapes how the model responds.
3. Key Differences Between RAG and Fine-Tuning
Although both enhance model performance, they solve different categories of problems.
RAG modifies the input
→ It feeds the model fresh, targeted information.
Fine-tuning modifies the model itself
→ It changes how the model thinks and responds.
This difference leads to several practical distinctions.
Update Frequency
RAG: Instant updates — change your data → new answers immediately
Fine-tuning: Must retrain whenever data changes
Knowledge Handling
RAG: Great for large documentation sets
Fine-tuning: Not useful for storing long documents
Cost and Complexity
RAG: Low cost; simple to maintain
Fine-tuning: More expensive and requires ML expertise
Control Over Style and Structure
RAG: Limited
Fine-tuning: Very high
4. When RAG Is the Right Choice
RAG is the best solution when your goal is to give an AI system accurate answers based on current or private information.
Below are the most common RAG use cases.
Use Case 1: Knowledge Base Question-Answering
If you want your chatbot to answer questions using:
PDFs
SOPs
Product catalogs
Policies
Research papers
Internal documentation
Then RAG is ideal because it retrieves the exact paragraphs needed to answer the question.
Use Case 2: Customer Support Automation
RAG ensures responses use approved, traceable, and organization-specific content.
This is essential for industries like:
Healthcare
Banking
Education
Government
Use Case 3: Compliance or Safety-Critical Workflows
When accuracy and traceability matter, RAG provides a safer system because it returns:
Answer + Sources.
This reduces hallucinations and ensures every response is backed by real data.
Use Case 4: Rapidly Changing Knowledge
If your business updates:
Policies
Pricing
Features
Product specs
Instructions
RAG handles these changes without retraining the model.
5. When Fine-Tuning Is the Right Choice
Fine-tuning is ideal when your problem is not about retrieving new information but about making the model behave in a certain way.
Use Case 1: Enforcing a Writing Style
If you want consistent responses that match:
A brand voice
A teaching style
A persona
A corporate tone
Fine-tuning is perfect.
Use Case 2: Classification and Labeling Tasks
Fine-tuned models perform extremely well for:
Intent classification
Sentiment detection
Ticket routing
Document tagging
These tasks depend on patterns, not specific facts.
Use Case 3: Repetitive Formatting
If every output must follow a strict format:
JSON structure
Tables
Bullet points
Step-based templates
Fine-tuning improves reliability.
Use Case 4: Reducing Prompt Length and Cost
A fine-tuned model:
Needs fewer tokens
Responds more consistently
Avoids complicated prompting
This results in lower operating cost.
6. Situations Where Both Are Needed
Many high-performing enterprise systems use both RAG and fine-tuning.
Example: Customer Support AI
-
Fine-tuning: Teaches tone, structure, escalation rules
-
RAG: Supplies updated policies and documentation
Example: Technical Analysis Assistant
-
Fine-tuning: Teaches reasoning steps
-
RAG: Provides real-time market data or documentation
Example: Enterprise Chatbot
-
Fine-tuning: Reduces prompt complexity
-
RAG: Ensures factual grounding
Combining both leads to a more powerful and stable system with better user experience.

7. Decision Framework: RAG or Fine-Tuning?
Use this simple guide:
✔ Choose RAG when:
The answer depends on documents
Knowledge changes frequently
You need source citations
You want lower cost and easy updates
✔ Choose Fine-Tuning when:
You need a specific tone or style
You want consistent formatting
You have lots of training examples
Your task is pattern-based, not fact-based
✔ Choose Both when:
You need accurate answers and controlled behavior
If you ask:
“Does the model need new knowledge or a new behavior?”
You’ll know exactly which method to choose.
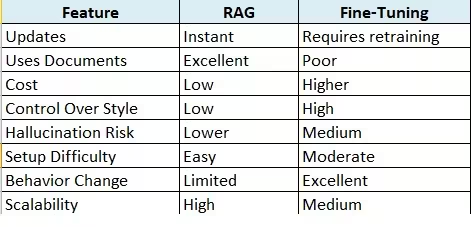
8. Pros and Cons Comparison Table
Financial Services
A bank uses RAG to answer compliance questions using internal documents. Fine-tuning is used to enforce a consistent support style.
Healthcare
RAG retrieves clinical guidelines. Fine-tuning shapes the tone to be empathetic and safe.
E-commerce
RAG pulls product information. Fine-tuning ensures responses match the brand voice and writing standards.
These examples show that the best solution depends on whether you’re managing knowledge, behavior, or both.
10. Conclusion
RAG and fine-tuning are not competing technologies; they are complementary tools for improving AI performance. RAG gives models access to fresh, external knowledge, while fine-tuning adjusts the model’s internal reasoning and behavior.
If your goal is accurate responses based on real documents, choose RAG.
If your goal is stable, stylistic, or structured behavior, choose fine-tuning.
And if you want both reliability and precision, combine them for the best results.
- Choosing the right approach will help you build AI systems that are scalable, trustworthy, and aligned with real business needs.
